Jenkins doesn't start VMs
Scenario
You configured Anka Build Cloud alongside the Jenkins plugin. You are now trying to run a job but it doesn’t start and you are not seeing any new Nodes connected to Jenkins.
Note
When Jenkins starts a job using the Anka plugin, a lot of times you will see this message:
‘Jenkins’ doesn’t have label ‘MyLabel’
This is just the way Jenkins says it doesn’t have available nodes with this label at the moment.
It doesn’t mean that there are no nodes or clouds configured with this label.
Common reasons
- Configuration mistakes
- SSH port forwarding not set correctly on VM
- JNLP port is not accessible from VM
- Outdated Jenkins environment
- VM has different version of Java from the Master
- The Anka Cloud can’t run VMs (see VM is stuck at scheduling)
If you are not sure that your cloud can run VMs, it’s a good place to start.
Go to your dashboard and start a VM Instance.
If it starts and you can connect to it, the problem is probably around Jenkins configuration or compatibility with Jenkins.
If your VM does not start try to troubleshoot it
Configuration mistakes
Since there are many configuration options in Jenkins Anka Build plugin, we can sometimes miss one or make a mistake. Also, the feedback given to the user is mainly using logs.
Let’s go over the most important configuration parameters, and check that everything is configured correctly.
Anka Build Controller URL
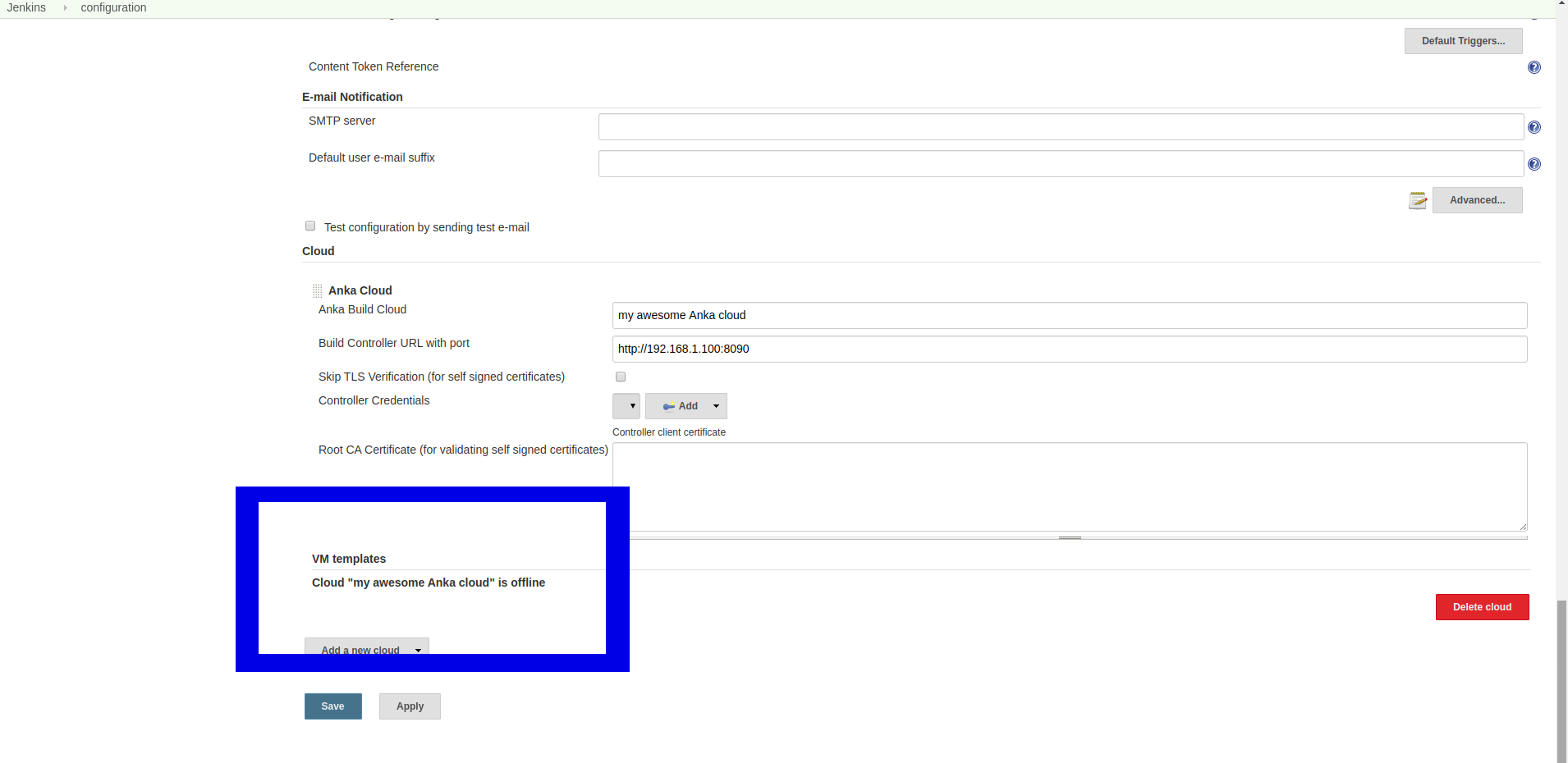
Go to Manage Jenkins -> Configure System, and scroll all the way down to the clouds section.
If your address is wrong, or your cloud is offline, you should see a message saying “Cloud XXX is offline” just like in the image below (marked in a blue rectangle).
A sign that the Controller URL is configured properly: you are able to select an Image.
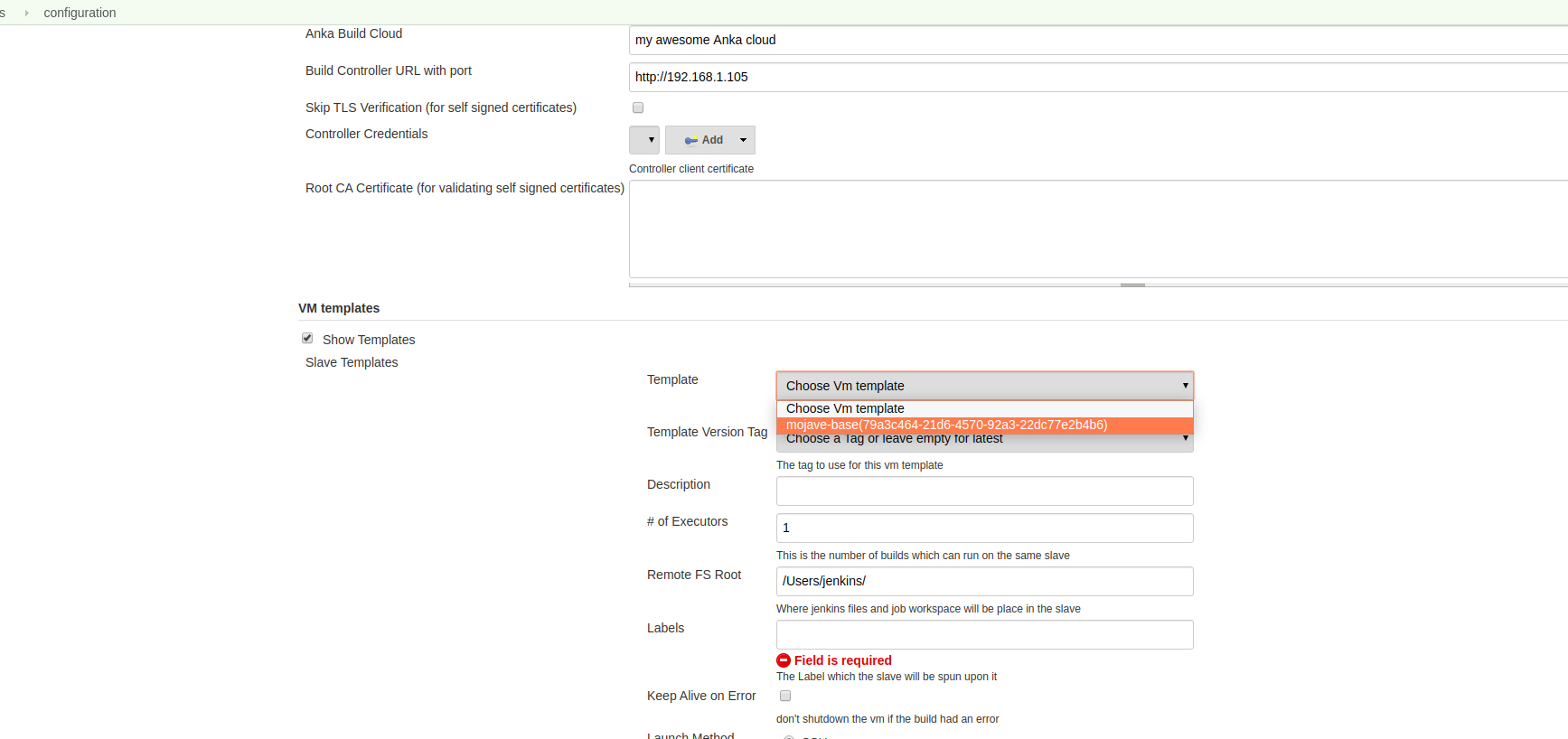
Remote FS Root
Remote FS Root is required to be a valid writable path on the VM in order for Jenkins to run the node.
You can find it in the slave template configuration.
If you are unsure of what this value should be, it’s best to set it to the home folder of the user that Jenkins will run as.
For example: when using the user anka set Remote FS Root to /Users/anka.
Labels
Make sure the labels configured in your slave template match the ones you are using in your builds.
Also check that none of your other nodes has the same label.
Clone’s user
When using SSH as the launch method, make sure that Jenkins is connecting to your VM with the right user and credentials.
SSH port forwarding not set correctly on VM
When using SSH as the launch method, port forwarding is used to connect to the VM through the host it runs on.
You can find more information on how set up port forwarding here
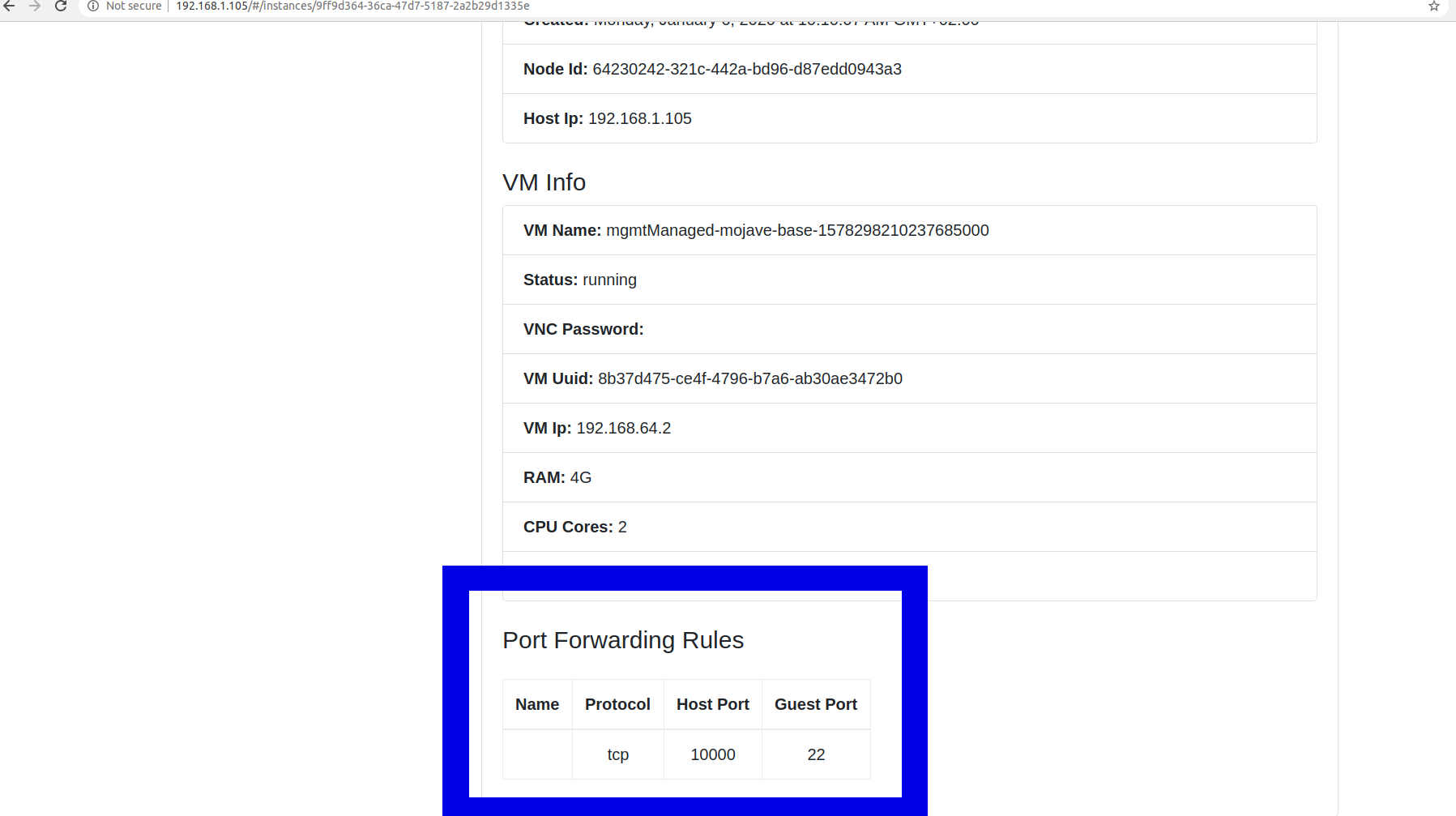
To check if port forwarding is set correctly, start a new VM Instance from the Anka Cloud Dashboard.
After the VM Instance is in state Started and VNC connection string has a value, click on the Node Name in the Instance row to see it’s details.
In the bottom pane, look at port forwarding rules. If nothing is there and the VM has an IP, it means that port forwarding needs to be configured (see screenshot).
You might have to wait a little bit for the VM to have it’s network ready, refresh the page if necessary.
Note
When configuring port forwarding for Jenkins –host-port should be configured to 0.
Setting the host port to 0 enables automatic assignment. This is done to make sure that VMs on that host will be available on different ports.
JNLP port is not accessible from VM
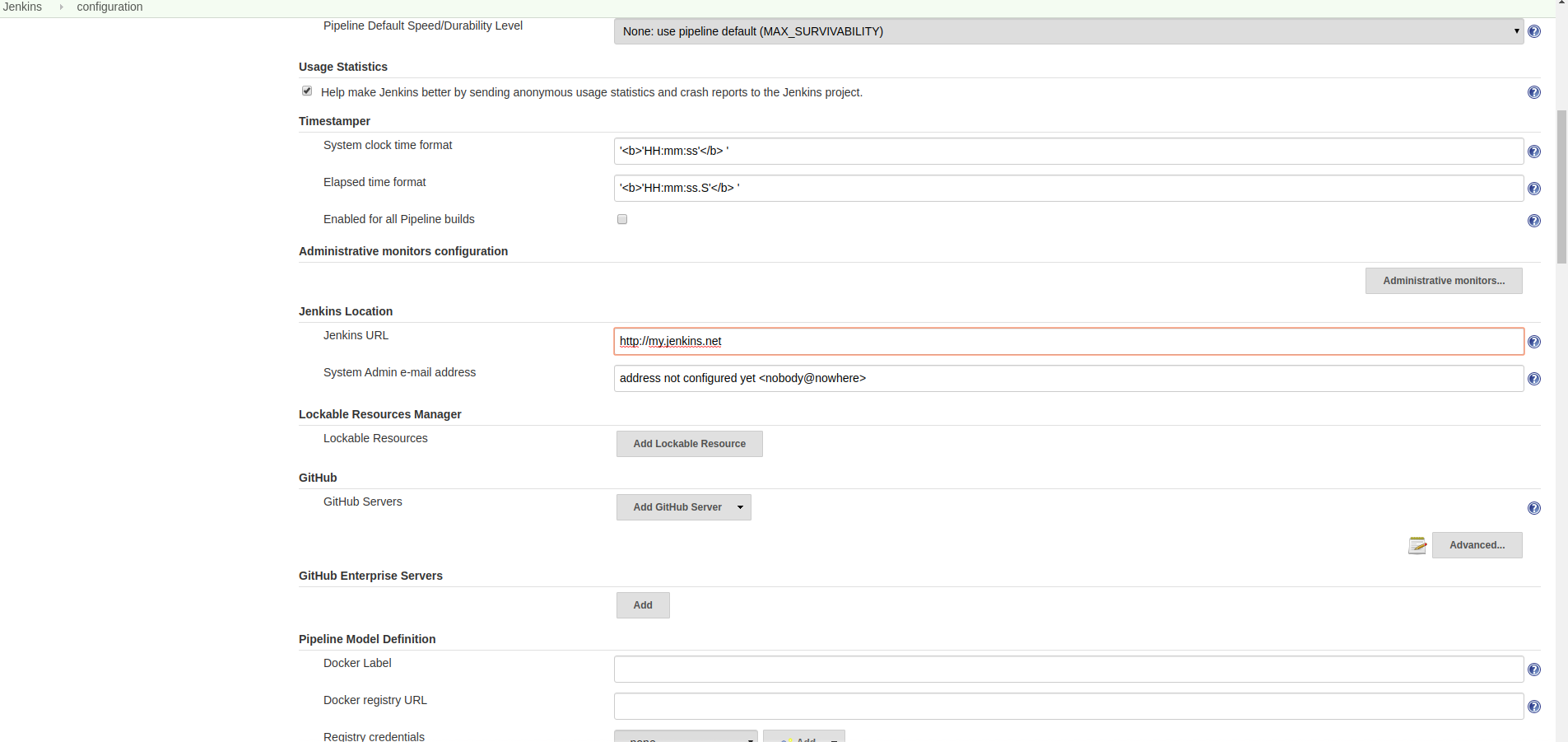
Make sure the Jenkins URL is set in the configuration page
Go to Manage Jenkins -> Configure System, and scroll down to Jenkins Location. Check that Jenkins URL is correct.
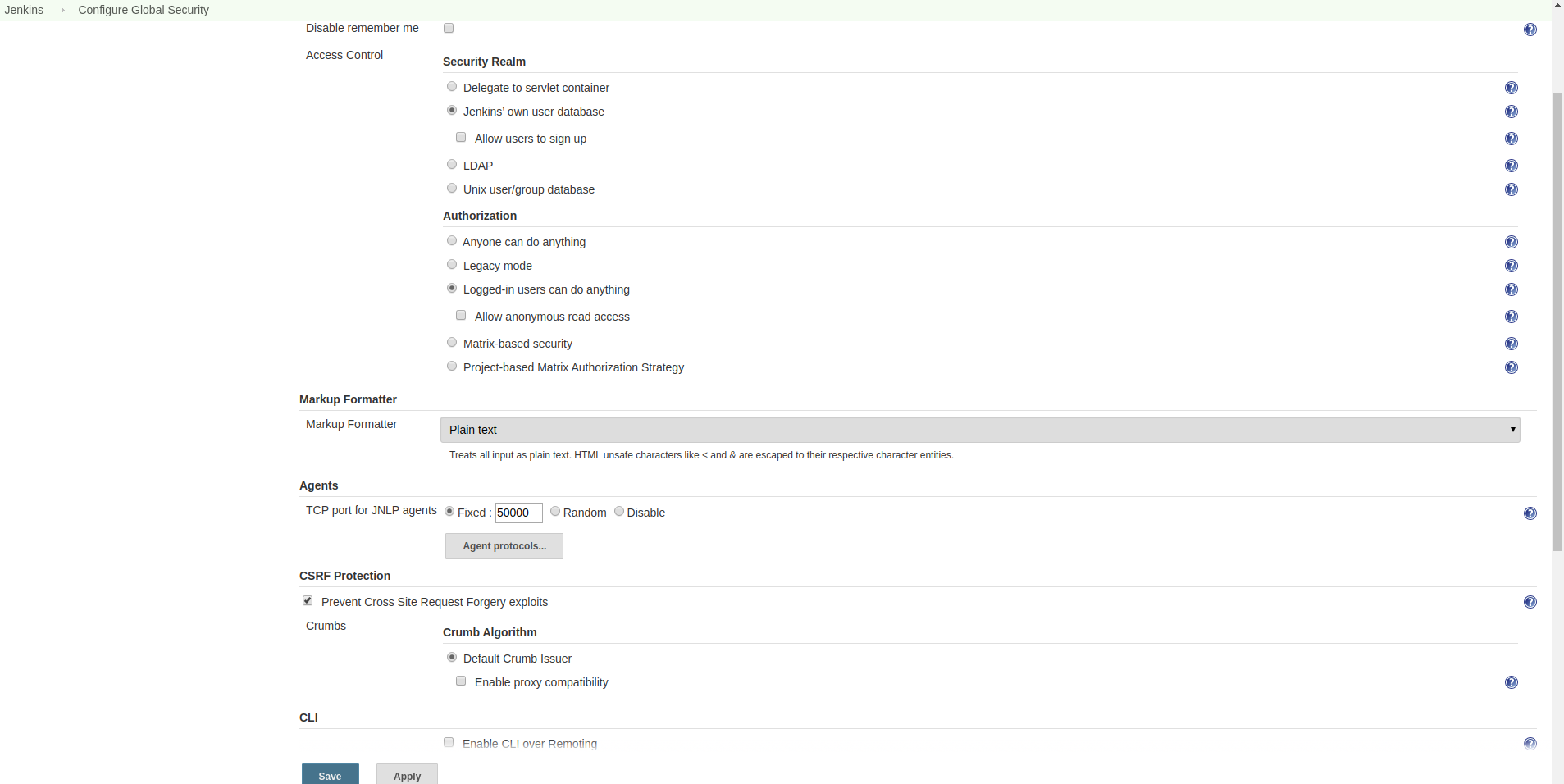
Check that JNLP port is enabled
Go to Manage Jenkins -> Configure Global Security, and scroll down to Agents.
Check that TCP port for JNLP agents is not set to disabled
Check JNLP log on the VM
The VM writes a log when trying to connect to Jenkins via JNLP. The location of this log on the VM is /tmp/log.txt.
In order to log at the log you’ll have to “catch” it when the VM tries to connect to Jenkins.
Start the job that would start the VM and go to your Anka Cloud dashboard. When the VM is started, SSH to it or connect to it via VNC and open the terminal.
Execute the tail command to view the log:
tail -f /tmp/log.txt
You can also check connectivity to Jenkins’s JNLP port.
Replace
example.jenkins.comwith your Jenkins hostname or IP and50000with the JNLP port configured for your server.
# Successful connection
nc -v example.jenkins.com 50000
found 0 associations
found 1 connections:
1: flags=82<CONNECTED,PREFERRED>
outif en0
src 192.168.64.2 port 49245
dst example.jenkins.com port 50000
rank info not available
TCP aux info available
Connection to example.jenkins.com port 50000 [tcp/*] succeeded!
# Failed connection
nc -v example.jenkins.com 50001
nc: connectx to example.jenkins.com port 50001 (tcp) failed: Connection refused
Outdated Jenkins environment
Jenkins uses a library to handle master <> agent communication. Broken communication between Jenkins and it’s agents can be sometimes fixed by upgrading Jenkins to a version with a newer remoting library.
Browse the Jenkins changelog and look for an update in remoting library.
VM has different version of Java from the Master
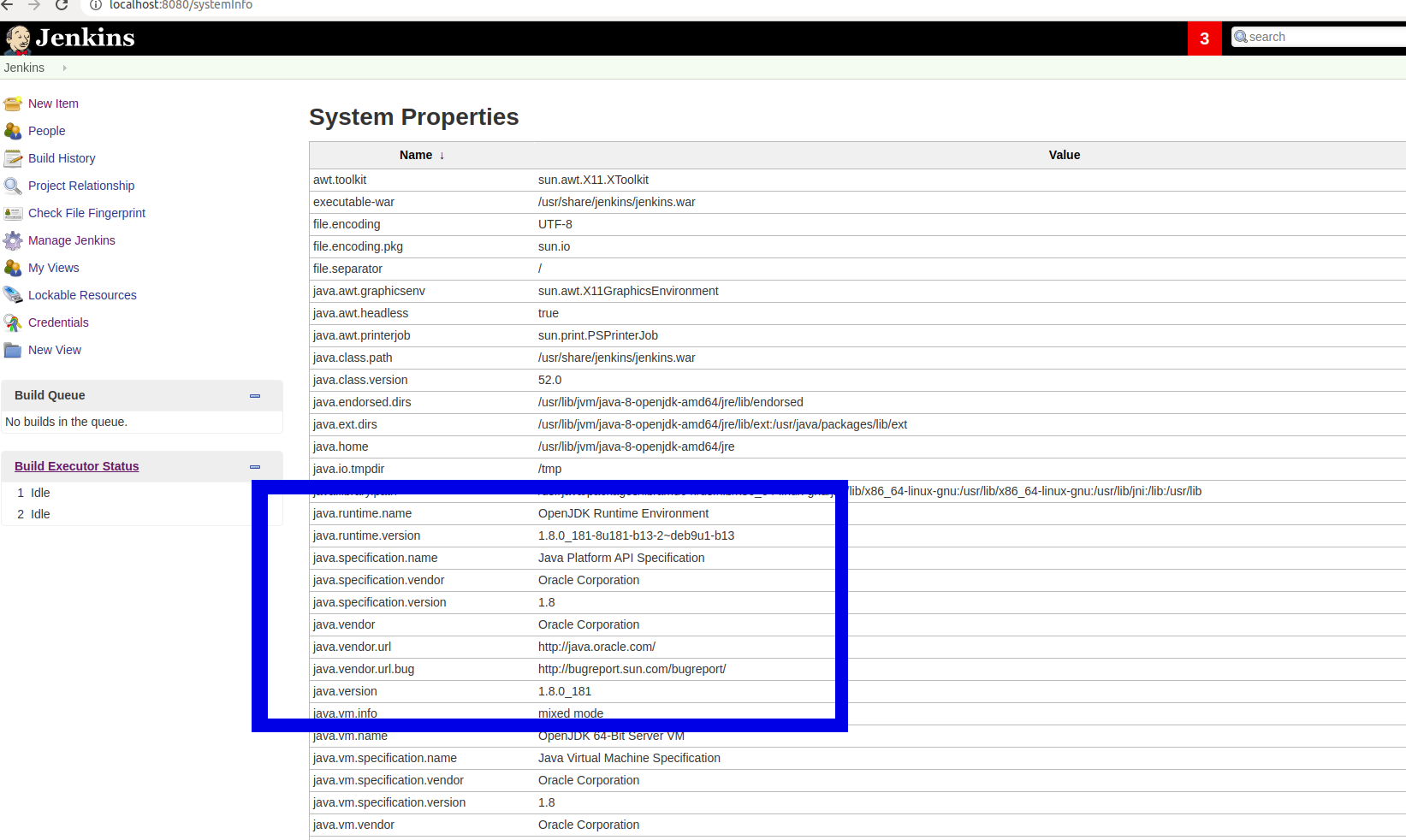
Check your Jenkins’s host Java version
Go to Manage Jenkins -> System Information, look at the Java version parameters.
Check the Java version on the VM matches
If you don’t have a VM running, start the job that would start the VM and go to your Anka Cloud dashboard. Then wait for the VM to be started.
SSH to the VM or connect to it via VNC and open the terminal.
Execute the java -version command:
java -version
java version "1.8.0_201"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_201-b09)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.201-b09, mixed mode)
If the Java versions on the Jenkins host and the VM does not match. Install the correct version of Java on the VM.