Starting and Accessing your VM
Prerequisites
- You’ve installed the Anka Virtualization package
- You’ve got an active license
- You’ve created your first VM Template
When running Anka commands on your machine, ensure that you have an active login session (you might have to VNC in if you’re connected over SSH) and also have enabled automatic login for the current user:
System Preferences > Users > Enable automatic login
Anka Start
With the UI
Launch the Anka application found under /Applications. Once launched, you will see the VM Template on the right sidebar. You can double click the VM to not only start it but also launch the Anka Viewer window.

With the CLI
To start the VM in headless mode: sudo anka start {vmNameOrUUID}
sudo anka start --view {vmNameOrUUID}will start the VM and launch the Anka Viewer window.
❯ anka start 11.0.1
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| uuid | 55b27ccc-81e2-47e3-9702-e678540f7219 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| name | 11.0.1 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| created | Sep 01 08:30 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| cpu_cores | 4 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| ram | 8G |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| display | 1 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| hard_drive | 128Gi (17.9Gi on disk) |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| addons_version | 2.3.0 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| status | running |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| mac | 76:f5:d8:dd:63:bc |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| vnc_connection_string | vnc://192.168.0.107:5900 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
Anka Run (exec)
Similar to docker exec, anka run allows execution of commands inside of a VM.
> sudo anka run --help
Usage: anka run [OPTIONS] VM_NAME COMMAND [ARGS]...
Run a command inside of a VM (will start VM if suspended or stopped)
Options:
-w, --workdir PATH Working directory inside the VM
-v, --volume PATH Mount a host directory into VM
-n, --no-volume Use this flag to prevent implicit mounting of current folder(see --volume option and the
implicit_mount config paramerer).
-E, --env Inherit environment variables ('--env' is the deprecated form)
-e TEXT Provide an environment variable in overriding mode
-f, --env-file PATH Provide environment variables from file
-N, --wait-network Delay execution until guest network interface is fully up
-T, --wait-time Delay execution until guest time syncs
--help Display usage information
If the VM is in a suspended or stopped state,
anka runwill start it.
Catalina and lower: When running
anka runwith no options/flags, it will mount the current directory from the host into the VM and execute commands in this mounted location. This can be disabled using the-noption.
Big Sur: When running
anka runwith no options/flags, the current directory will not be mounted in by default. This requires the manual installation of addons
Once started, you can use anka run on the host terminal to validate things are working properly:
❯ anka run 11.0.1 bash -c "hostname && ls -l && ping -c 5 google.com"
Mac-mini.local
total 102872
drwxr-xr-x 13 anka staff 416 Aug 31 10:35 _diag
drwxr-xr-x 7 anka staff 224 Aug 31 10:35 _work
-rw-r--r-- 1 anka staff 52630785 Aug 28 10:12 actions-runner-osx-x64-2.273.0.tar.gz
drwxr-xr-x 230 anka staff 7360 Aug 19 07:49 bin
-rwxr-xr-x 1 anka staff 2673 Aug 19 07:48 config.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 anka staff 623 Aug 19 07:48 env.sh
drwxr-xr-x 3 anka staff 96 Aug 19 07:49 externals
-rwxr-xr-x 1 anka staff 1666 Aug 19 07:48 run.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 anka staff 3280 Aug 28 10:12 svc.sh
PING google.com (172.217.10.110): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 172.217.10.110: icmp_seq=0 ttl=114 time=18.919 ms
64 bytes from 172.217.10.110: icmp_seq=1 ttl=114 time=24.834 ms
64 bytes from 172.217.10.110: icmp_seq=2 ttl=114 time=16.992 ms
64 bytes from 172.217.10.110: icmp_seq=3 ttl=114 time=23.158 ms
64 bytes from 172.217.10.110: icmp_seq=4 ttl=114 time=25.797 ms
--- google.com ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 16.992/21.940/25.797/3.416 ms
The
anka runcommand doesn’t source .profile or .bash_profile. You have to source the file before executing other commands
To inherit the host’s environment, use
anka run --envcommand. However, existing VM variables will not be overridden by host’s variables. You can also pass them inside of a file likeanka run --env-file environment.txt, where environment.txt is a text file in the formVARIABLE=VALUE, one variable per line.
An advanced usage example of
anka runinside of a bash script can be found in our Getting Started Repo’s Tag Creation Script
Anka View
On Big Sur, many of the resolution/graphics features in Anka View do not work unless you manually install addons
> sudo anka view --help
Usage: anka view [OPTIONS] VM_ID
Open VM in Anka Viewer
Options:
-d, --display INTEGER Specify the displays to view
--screenshot Make png screenshot
--click Send HDI events
--click-rec Record HID events
--help Display usage information

You can set the resolution of the VM under the
Apple Menu > View. Or, you can use the Live Resolution and Enter Fullscreen.
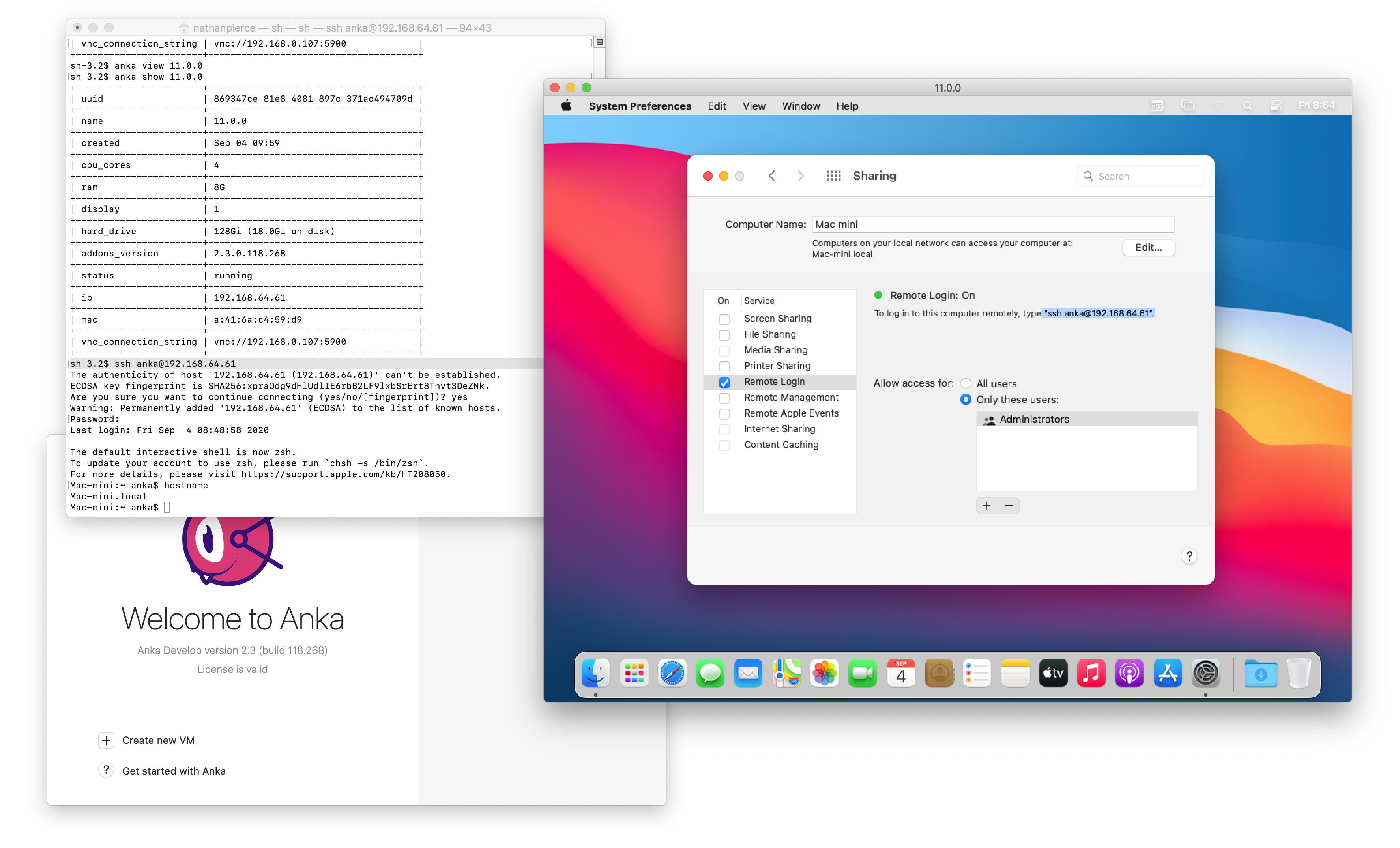
SSH
In order to SSH into the VM, you’ll need to enable Remote Login under System Preferences > Sharing (enabled by default). Next, check that networking has fully started on the VM by running anka show {vmNameOrUUID}:
❯ anka show 11.0.1
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| uuid | 55b27ccc-81e2-47e3-9702-e678540f7219 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| name | 11.0.1 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| created | Sep 01 08:30 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| cpu_cores | 4 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| ram | 8G |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| display | 1 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| hard_drive | 128Gi (18.2Gi on disk) |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| addons_version | 99.9.0.118.19306 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| status | running |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| ip | 192.168.64.49 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| mac | 76:f5:d8:dd:63:bc |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| vnc_connection_string | vnc://192.168.0.107:5900 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
If you do not see the row ip, then networking has not fully been started yet.
Once you do see an ip, you can then SSH with the user and ip: ssh anka@{ip}
We provide a fixed IP inside of the VM for accessing the host:
192.168.64.1(or192.168.128.1for “host” type) (not available with VM network isolation enabled)
VNC
By default, without any modifications to the VM post-create, you’ll be able to access the VM with VNC using the vnc_connection_string under a started VM’s anka show output:
❯ anka start 10.15.6
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| uuid | c0847bc9-5d2d-4dbc-ba6a-240f7ff08032 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| name | 10.15.6 (base) |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| created | Sep 25 14:02 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| cpu_cores | 6 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| ram | 10G |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| display | 1 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| hard_drive | 80Gi (14.5Gi on disk) |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| addons_version | 2.2.3.118.804 (update recommended) |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| status | running |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| mac | aa:2c:55:82:9e:8c |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
| vnc_connection_string | vnc://:admin@192.168.0.110:5900 |
+-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
However, this is a very limited VNC with no extensions (copy/paste, extended authorization, etc). To use Apple’s VNC with all extensions enabled, you’ll need to anka view into the VM and enable Screen Sharing under System Preferences (kickstart scripts will not work for Big Sur and above). Once enabled, you need to stop the VM with anka stop, then use the modify command to set port-forwarding of the VNC port from within the VM to a port on the host. This will allow you to VNC to the host IP and the forwarded port (usually 10000-10005).
When using a Linux or Windows VNC client like RealVNC, ensure it’s using TrueColor settings (32 bit), not 256 colors (indexed). This may be called “Picture Quality” in your client (set it to Medium).
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
anka rundoesn’t support TTY mode, but you could easily use POSIX streams as with regular bash tool:anka run -n VNMANE whoami > /dev/null cat file.txt | anka run -n {vmNameOrUUID} md5- You can set the resolution of the Anka Viewer using
sudo anka modify 10.15.4 set display --resolution 1200x800 - Port forwarding of VM ports is supported